Deep neural network sentence encoders can be a very powerful tool to help you automate the process of reviewing and applying an inhuman number of potential invalidating references against a set of subject patent claims. After a search is conducted, the sentences and paragraphs of the resulting patents and publications can be automatically compared against the specific claim language of the subject patent. A full analysis of the search results may indicate even stronger patents or combinations of patents to apply against a subject patent claims than the art of record, or may help to confirm the strength of the subject patent claims relative to a larger collection of art references than originally cited during prosecution.
All in Due Diligence
Using Deep Neural Networks to Find the “Best” Known Cited Art and Create Claim Charts
When initially reviewing a patent portfolio to understand its scope, it is helpful to understand the universe of art that has already known in the portfolio. When there are a large number of known art references, it is extremely helpful to be able to focus on the "best" art that is of record. Using deep neural network sentence encoders, we can automate the discovery of the "best" parts of the known art.
Using Deep Neural Networks to Analyze Priority Claims to Provisional Applications
However, often provisional applications are not as detailed as the later filed non-provisional applications. The patent claims are only entitled to the date of the provisional application for material that was disclosed in the provisional; not new matter that was added in a later filed non-provisional application. Like the analysis that was performed in the article Using Deep Neural Networks to Automate the Creation of Specification Support Charts, Deep neural network can also be used to help analyze priority claims to provisional applications.
Using Deep Neural Networks to Analyze Specification Support and Automate the Creation of Specification Support Charts
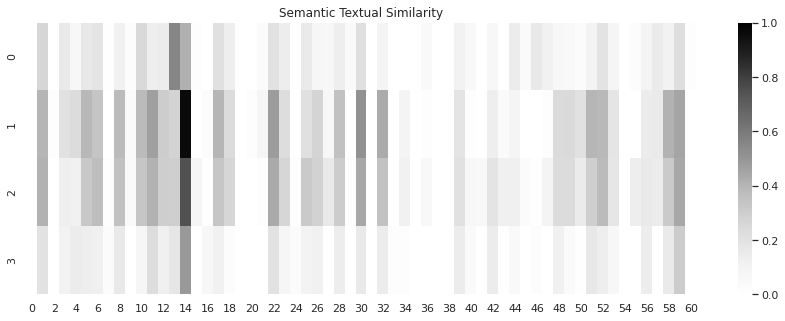
A heat map display can be used to easily visualize where claim elements are supported in the specification. The darker the color intersecting cells represent more similarity between the specification and the claim language. To the extent the heat map does not have a high level of similarity to the claims, it may indicate that there is an issue with specification support for a particular claim or claim element. This information can be used to automate the creation of a more traditional claim support chart.
Using Deep Neural Networks to Streamline Patent Prosecution and Litigation Tasks
Patent prosecution and litigation tasks can be streamlined and improved using deep neural networks trained to determine semantic similarity between sentences. In the next series of articles, I will discuss using this type of sentence encoder deep neural network for various patent related tasks including.